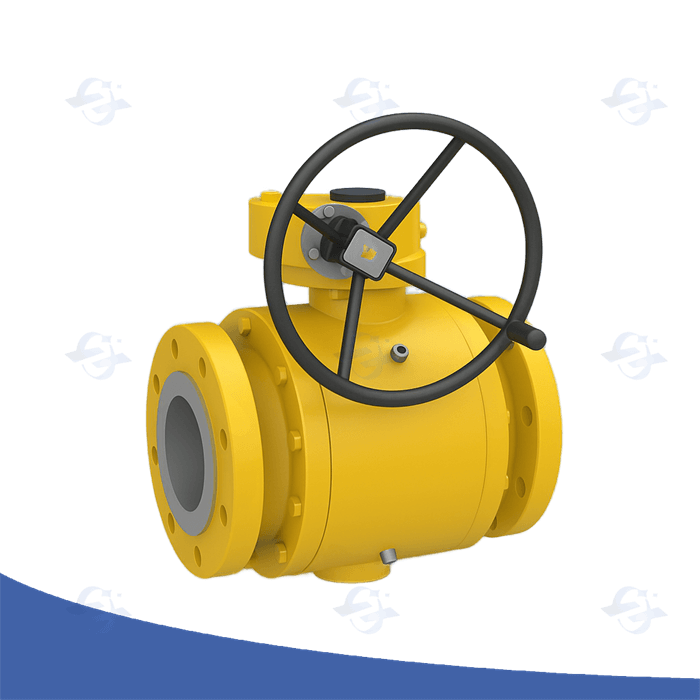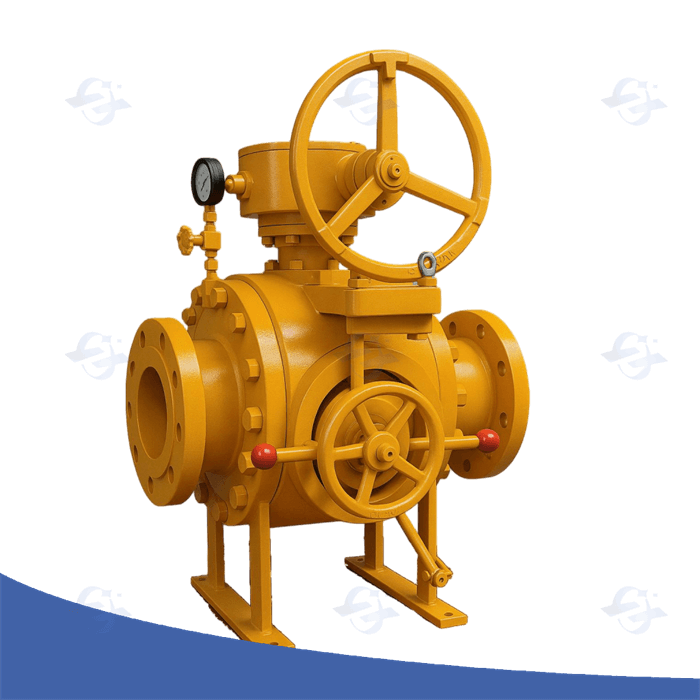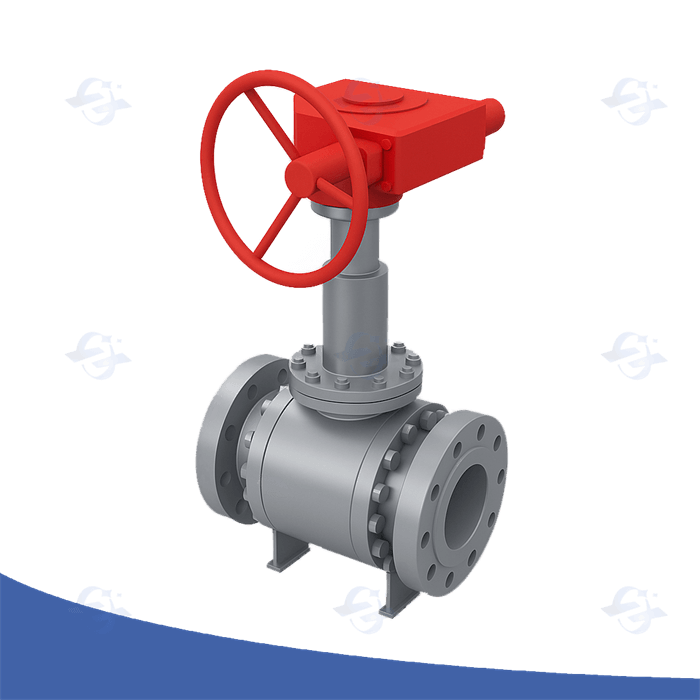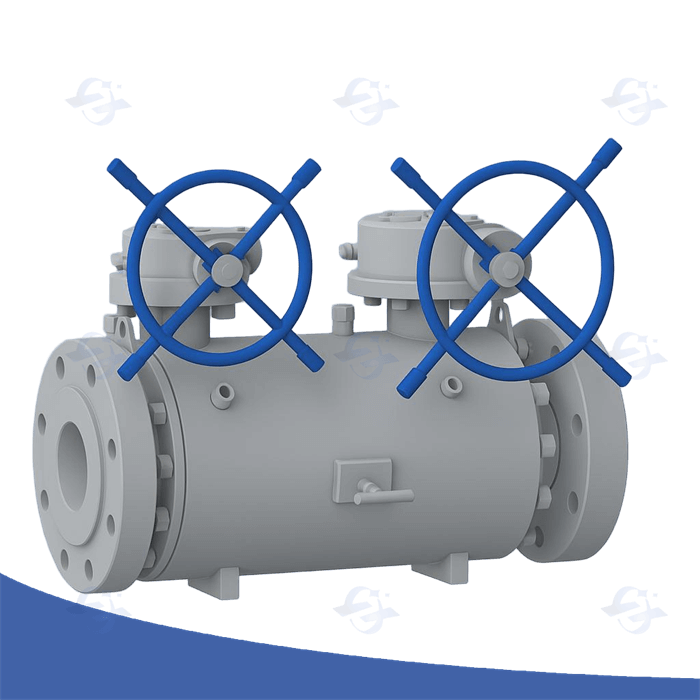
A Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve is a critical component used in many industries, especially in oil and gas, petrochemical, and chemical processing plants. It plays a vital role in providing safety and ensuring system integrity by isolating and venting pressurized systems. In simple terms, a DBB valve is designed to isolate a section of piping or equipment from both upstream and downstream pressures while providing a venting option in between the isolation points.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about DBB valves: their design, operation, applications, advantages, and considerations for selection.
What is a Double Block and Bleed (DBB) Valve?
A DBB valve is a specialized valve that combines two isolation valves and a bleed valve into one compact valve assembly. It is designed to isolate a system by blocking the flow in both upstream and downstream directions and then providing a means to vent or drain any fluid or gas trapped between the isolation valves.
The core design of a DBB valve typically consists of:
Two Isolation Valves: These valves are positioned upstream and downstream of the section being isolated, ensuring complete isolation.
A Bleed Valve: The bleed valve, located between the two isolation valves, is used to vent or drain any accumulated fluid or gas that could build up in the isolated section.
The primary purpose of a DBB valve is to create a safe, sealed environment for maintenance, testing, or other operational purposes by isolating a section of the pipeline or system.
How Does a DBB Valve Work?
Isolation: The DBB valve has two separate isolation valves. The first valve isolates the upstream pressure, and the second valve isolates the downstream pressure. Both valves must be closed to ensure full isolation.
Bleed Function: Once the isolation is complete, the bleed valve can be opened to vent any trapped fluid or gas between the two isolation valves. This ensures that any residual pressure is safely released, preventing the build-up of hazardous or unwanted fluids between the isolation points.
Safety and Maintenance: The combination of isolation and venting functions allows operators to safely maintain or test the isolated section without being exposed to the potential hazards of pressure or fluids. For instance, it’s often used before maintenance work to ensure that the section is completely depressurized.
Design Variations of DBB Valves
There are different design variations of DBB valves, depending on the specific application requirements. Some common types include:
Ball Valve DBB: These use ball valves for isolation. Ball valves offer quick, reliable sealing and are used in applications where high-flow capacity and fast operation are essential.
Gate Valve DBB: Gate valves are commonly used for larger pipe sizes or where a full flow of fluids is required. They provide a tight shutoff but are slower to operate compared to ball valves.
Check Valve DBB: In some systems, check valves may be used as part of the isolation design. These are often used in low-pressure systems where reverse flow needs to be blocked, and venting is necessary.
Double Block and Bleed with Needle Valves: In some cases, the bleed valve is a needle valve, offering more precise control over venting and draining small amounts of trapped fluids or gases.
Key Benefits of DBB Valves
Increased Safety: One of the primary advantages of a DBB valve is the added safety it provides. It ensures that no hazardous or pressurized fluid is left in the system between the isolation points, reducing the risk of leaks, accidents, or explosions during maintenance or inspection.
Prevention of Contamination: The double isolation system helps prevent cross-contamination between upstream and downstream systems. This is especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing, where contamination can have serious consequences.
Simplifies Maintenance: DBB valves make maintenance, testing, and servicing easier and safer by providing a clear method of isolating sections of pipelines without disrupting the entire system. Maintenance workers can be confident that the section is depressurized and free from hazardous materials before proceeding.
Versatility: DBB valves can be used in a wide variety of applications, including high-pressure systems, gas pipelines, chemical reactors, and other critical systems. They are designed to handle liquids, gases, and even corrosive fluids.
Reduced Space and Complexity: Instead of installing multiple valves and fittings, a single DBB valve can provide isolation, venting, and safety functions in one compact unit. This reduces the complexity of the piping system and saves installation space.
Leak Prevention: By ensuring that both upstream and downstream pressures are blocked and any trapped fluids are safely vented, DBB valves help to prevent leaks between isolated sections. This is particularly important in systems dealing with dangerous or toxic substances.
Common Applications of DBB Valves
Oil and Gas: DBB valves are frequently used in upstream oil and gas operations to isolate sections of pipelines for maintenance or inspection, ensuring safe and effective depressurization of pipelines and equipment.
Petrochemical Plants: In the petrochemical industry, DBB valves provide safety during maintenance and help ensure the integrity of critical pipelines carrying hazardous chemicals.
Chemical Processing: DBB valves are used to isolate reactors, vessels, and pipelines in chemical plants, allowing for safe testing, maintenance, or material handling without risking contamination or exposure to hazardous chemicals.
Water Treatment Plants: In water treatment facilities, DBB valves ensure that sections of the system can be isolated for maintenance or repair while ensuring that contaminants don’t enter the water supply.
Power Generation: DBB valves are used in power plants to isolate sections of steam, water, or gas pipelines during routine maintenance or emergency shutdowns.
Advantages Over Single Block Valves
Enhanced Safety: Unlike single isolation valves, DBB valves ensure full isolation from both sides, minimizing the chances of leakage or pressure-related accidents.
Reduces Need for Multiple Valve Installations: A DBB valve combines two isolation valves and a bleed valve into one unit, reducing the number of valves needed and simplifying system design and maintenance.
Improved Process Control: With two isolation points and a venting option, DBB valves provide better control over the process, ensuring that unwanted pressure buildup is safely managed.
Considerations When Selecting a DBB Valve
Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Ensure the DBB valve can handle the maximum pressure and temperature conditions of your system.
Material Compatibility: The materials of the valve should be compatible with the fluid or gas it will be handling to prevent corrosion, wear, or degradation over time.
Vent/Drain Capacity: Depending on the application, the capacity of the bleed valve to handle the volume of fluid or gas to be vented is an important consideration.
Size and Flow Requirements: Ensure that the DBB valve is appropriately sized to handle the flow rate of your system while ensuring minimal pressure drop.
Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the DBB valve meets industry standards, such as API, ASME, or ISO certifications, especially in critical systems like oil and gas or chemical processing.
Conclusion
The Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve is a vital component for safety, maintenance, and process control in industries requiring precise isolation of pipelines, vessels, and other systems. It provides a simple, efficient, and safe method for isolating, venting, and depressurizing sections of systems while preventing leaks and contamination. Whether used in high-pressure gas systems, chemical plants, or power generation, the DBB valve is an indispensable tool for ensuring operational safety and reliability.
By understanding the design, function, and advantages of DBB valves, industries can make informed decisions on how to incorporate them into their systems for improved safety and operational efficiency.