Ball Valve vs. Gate Valve: Advantages and Disadvantages
Valves are essential components in industrial piping systems, helping to regulate and isolate the flow of liquids and gases. Among the most commonly used valves are the ball valve and the gate valve. While both serve the purpose of starting and stopping flow, they differ in design, performance, and applications.
In this article, we provide a detailed comparison of ball valves and gate valves, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications.
1. What Is a Ball Valve?
A ball valve uses a spherical disc (the ball) with a hole through its center. When the hole is aligned with the pipeline, the valve is open; when rotated 90°, the valve is closed.
Key features of ball valves:
-
Quick quarter-turn operation
-
Excellent sealing performance
-
Compact structure

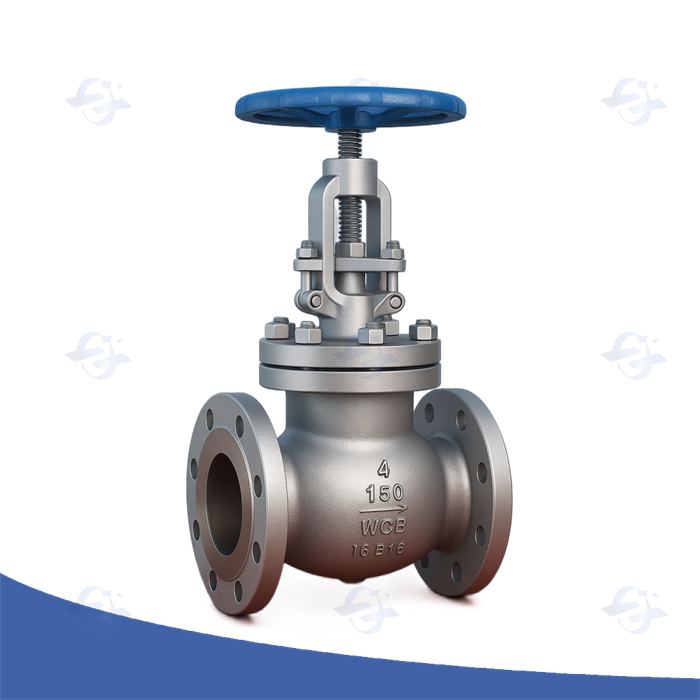
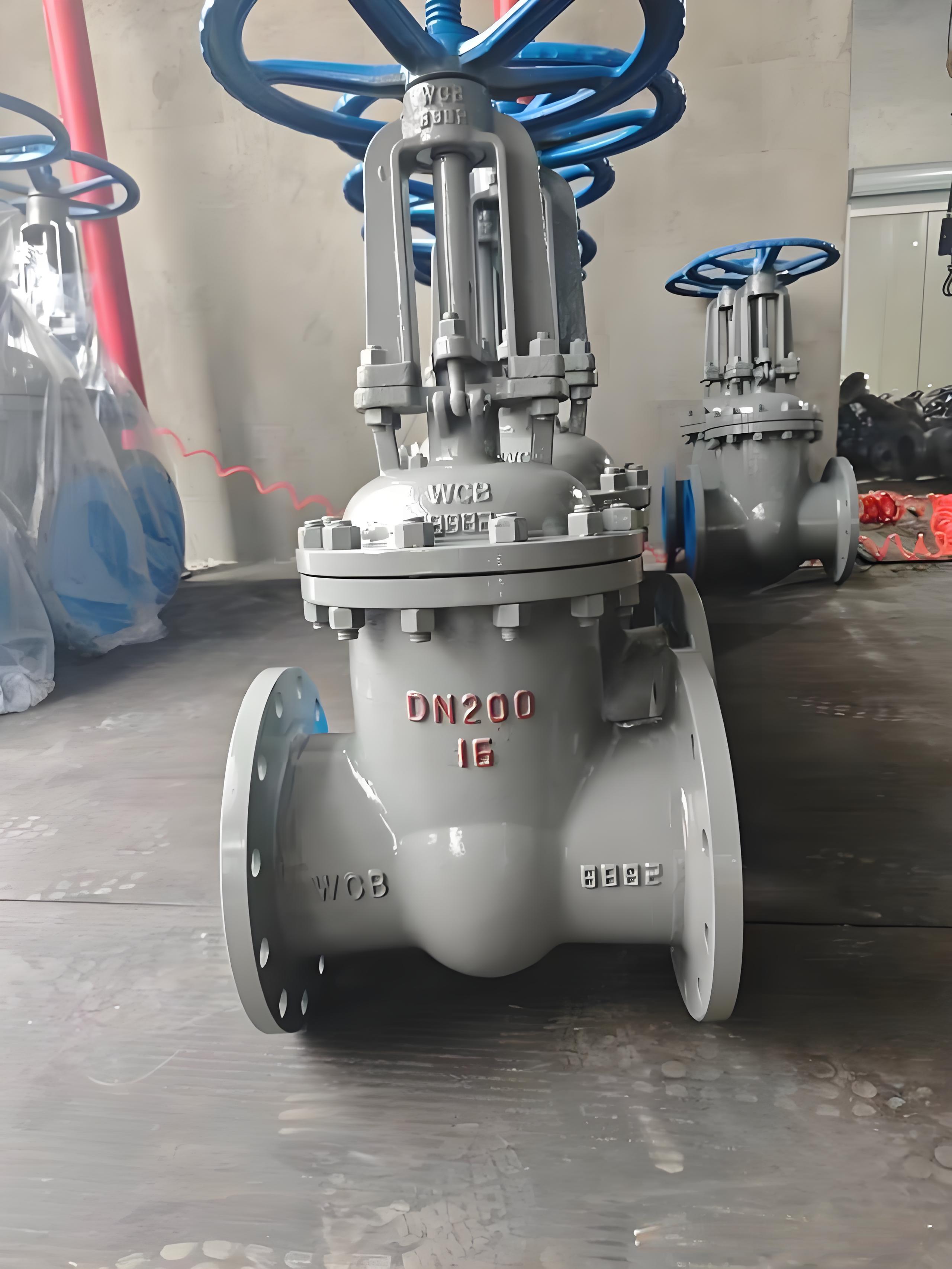
2. What Is a Gate Valve?
A gate valve uses a wedge-shaped gate (disc) that moves up and down perpendicular to the flow to start or stop the medium. It provides full bore flow when open, but requires multiple turns of the handwheel to operate.
Key features of gate valves:
-
Linear motion operation
-
Good for on/off isolation in large pipelines
-
Minimal pressure drop when fully open

3. Ball Valve vs. Gate Valve Comparison Table
| Feature | Ball Valve | Gate Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Quarter-turn (90°) | Multi-turn (slow opening/closing) |
| Sealing Performance | Excellent, bubble-tight shutoff | Good, but prone to slight leakage over time |
| Flow Control | Not ideal for throttling (causes seat damage) | Suitable for full open/close, not precise throttling |
| Pressure Drop | Very low, almost zero | Very low when fully open |
| Durability | Seats may wear under throttling | Gate can erode in high-velocity flow |
| Maintenance | Easy to operate and maintain | Larger, heavier, requires more space |
| Size Range | Common in small to medium diameters | Common in medium to large diameters |
| Cost | Generally higher than gate valves | Lower initial cost for large sizes |
| Applications | Oil & gas, chemical, natural gas pipelines, shutoff in critical systems | Water supply, wastewater, power plants, general isolation service |
4. Advantages and Disadvantages
✅ Advantages of Ball Valves
-
Quick and easy quarter-turn operation
-
Excellent sealing, suitable for gas and liquid shutoff
-
Compact design saves space
-
Minimal pressure loss
-
Reliable under high pressure and high temperature
❌ Disadvantages of Ball Valves
-
Not suitable for throttling service
-
Seat materials (like PTFE) may limit temperature range
-
More expensive for large diameters
✅ Advantages of Gate Valves
-
Ideal for full on/off isolation
-
Can be used in large-diameter pipelines economically
-
Minimal pressure loss when fully open
-
Robust design for general industrial service
❌ Disadvantages of Gate Valves
-
Slow operation (multi-turn)
-
Larger and heavier than ball valves
-
Not suitable for frequent operation
-
Sealing may deteriorate over time due to erosion
5. Which Valve Should You Choose?
-
Choose a Ball Valve if:
-
You need quick shutoff.
-
Leakage prevention is critical (e.g., gas pipelines).
-
Installation space is limited.
-
-
Choose a Gate Valve if:
-
You require infrequent operation for isolation.
-
The pipeline is large in diameter.
-
Cost is a key consideration.
-
Conclusion
Both ball valves and gate valves play important roles in industrial pipelines. Ball valves are favored for quick operation and tight sealing, making them ideal for oil & gas, chemical, and natural gas industries. Gate valves, on the other hand, are better suited for water supply, wastewater, and large-diameter isolation applications where slow operation is acceptable.
Ultimately, the choice between a ball valve and a gate valve depends on application requirements, cost considerations, and safety standards.