How to Choose the Right Valves for Natural Gas Pipelines
Natural gas pipelines operate under demanding conditions: high pressure, fluctuating temperatures, corrosive components, and strict safety requirements. Choosing the right valve is not simply a matter of matching size and pressure class—it’s a decision that directly affects system reliability, operational safety, and long-term maintenance costs.
From an engineering perspective, valve selection should always start from how the pipeline actually operates, not just from datasheets. Based on real-world project experience in natural gas transmission and distribution systems, the following factors are critical when selecting valves for gas pipelines.
1. Understand the Operating Conditions Before Anything Else
Before looking at valve types or brands, an engineer must clearly define the operating envelope of the pipeline.
Key parameters include:
-
Operating pressure and maximum allowable pressure (MAOP)
-
Operating temperature range
-
Gas composition (dry gas, wet gas, H₂S, CO₂ content)
-
Flow velocity and frequency of operation
-
Installation location (above ground, buried, offshore, station piping)
For example, dry natural gas in a transmission pipeline behaves very differently from wet gas with condensates. A valve that performs well in dry service may experience sealing problems or erosion in wet gas conditions.
Skipping this step is one of the most common causes of premature valve failure.
2. Selecting the Appropriate Valve Type
Different valve types serve different purposes in natural gas pipelines. There is no “one-size-fits-all” solution.
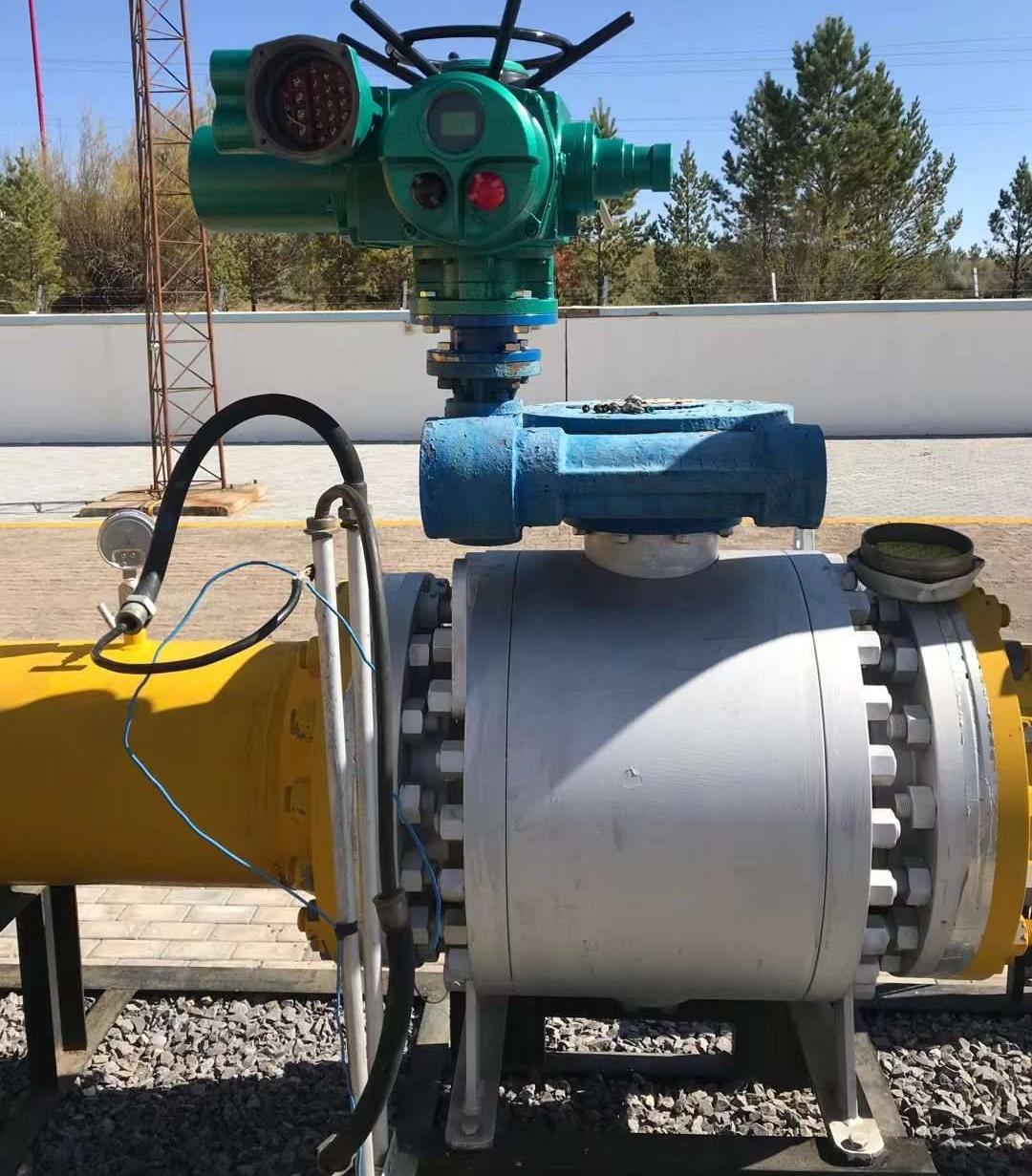
Ball Valves – Preferred for Isolation
Ball valves are widely used in natural gas pipelines, especially for on/off isolation service, because they offer:
-
Tight shut-off performance
-
Low pressure drop when fully open
-
Quick operation (quarter-turn)
-
Good suitability for pigging operations
For transmission pipelines, trunnion-mounted ball valves are typically preferred over floating ball designs due to better load distribution and reduced operating torque at high pressures.

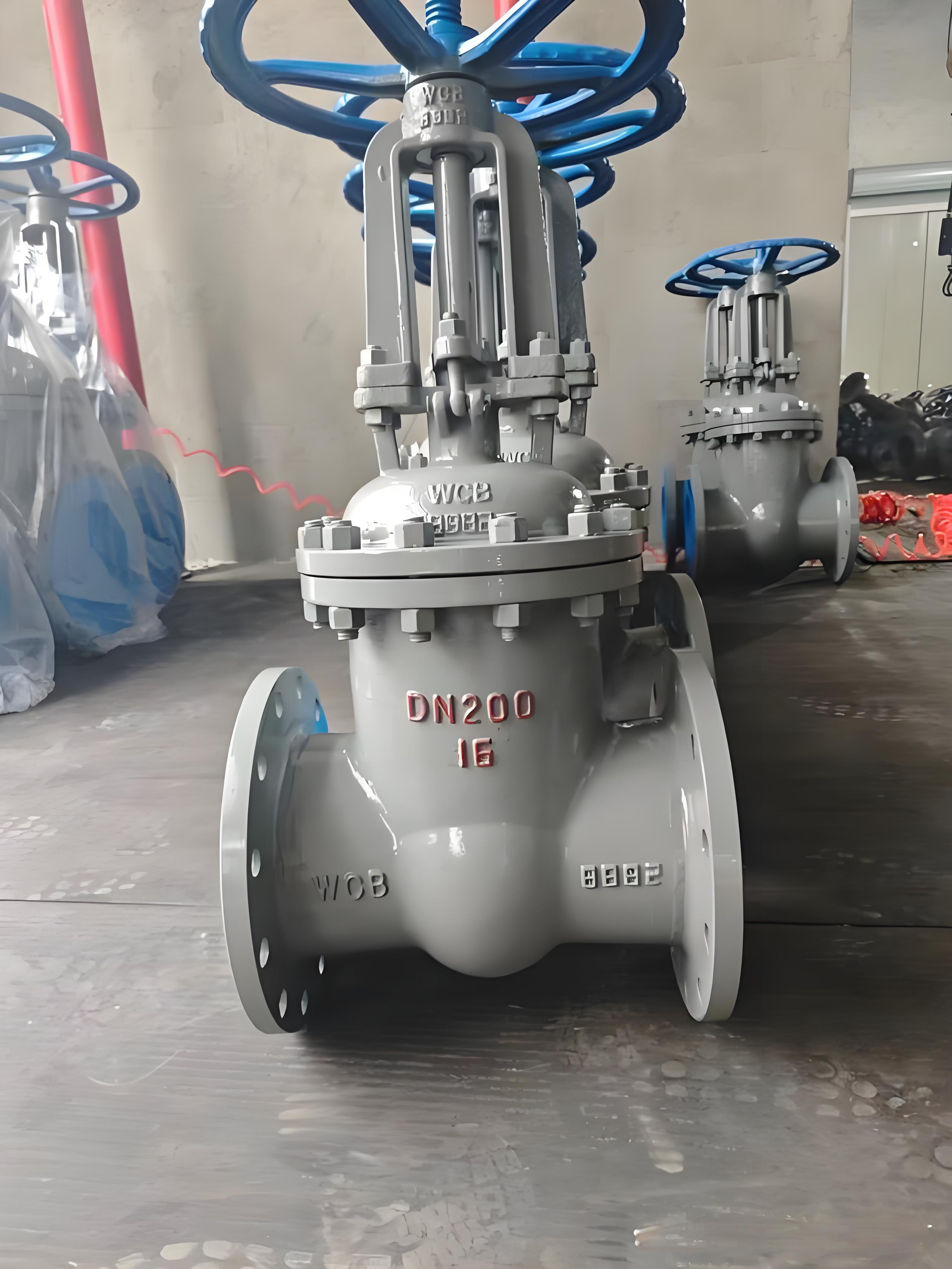
Gate Valves – Traditional but Still Relevant
Gate valves are commonly used in large-diameter pipelines where full bore and minimal flow restriction are required.
They are suitable for:
-
Infrequent operation
-
Full open or full close service
However, gate valves are not ideal for frequent operation and require careful attention to stem sealing and maintenance, especially in buried installations.

Plug and Butterfly Valves – Application-Specific
-
Plug valves are sometimes used in gas distribution systems due to good sealing performance but can require higher operating torque.
-
Butterfly valves, especially double or triple offset designs, may be suitable for low- to medium-pressure gas systems but are less common in high-pressure transmission lines.
The valve type should always match the function in the system, not just cost considerations.
3. Material Selection: More Than Just Pressure Class
In natural gas service, material selection is often underestimated.
Body and Trim Materials
Common Body & Trim materials include:
-
Carbon steel (ASTM A105, A216 WCB) for standard gas service
-
Low-temperature carbon steel (LTCS) for cold environments
-
Stainless steel or alloy steel for sour gas or corrosive conditions
If H₂S is present, NACE MR0175 / ISO 15156 compliance is not optional—it is mandatory.
Sealing Materials
Seat and seal materials must be compatible with:
-
Gas composition
-
Temperature range
-
Pressure cycling
For example, soft seats offer better sealing but may not be suitable for high temperatures or fire-safe requirements. Metal-seated designs are more robust but require precise machining and testing.
4. Compliance With Industry Standards and Codes
From an engineering and compliance standpoint, valves used in natural gas pipelines must meet internationally recognized standards.
Key standards include:
-
API 6D – Pipeline valves
-
ASME B16.34 – Valve design and pressure ratings
-
ISO 14313 – Pipeline valves
-
PED / CE (for European projects)
Compliance is not just about paperwork. These standards define design margins, testing procedures, and safety performance that directly impact pipeline integrity.
5. Actuation and Operation Considerations
Valve selection does not stop at the valve body.
Engineers must consider:
-
Manual vs. electric vs. pneumatic actuation
-
Required operating torque
-
Emergency shut-down (ESD) requirements
-
Fail-safe position (fail open or fail close)
In high-pressure natural gas pipelines, actuated ball valves with partial stroke testing are commonly used to ensure reliability without interrupting service.
Oversizing or undersizing actuators is a frequent engineering mistake that leads to slow response or mechanical damage.
6. Installation, Maintenance, and Lifecycle Cost
From a lifecycle perspective, the “cheapest valve” is often the most expensive over time.
Practical considerations include:
-
Accessibility for maintenance
-
Availability of spare parts
-
Ease of seal replacement
-
Proven performance history in similar projects
Engineers should always ask:
How will this valve perform after 10 or 20 years in service?
Field-proven designs with a clear maintenance strategy often outperform technically impressive but untested alternatives.
7. Engineering Judgment Matters More Than Datasheets
While specifications and standards are essential, engineering judgment remains irreplaceable.
A valve that looks perfect on paper may fail if:
-
The operating conditions were misunderstood
-
Installation constraints were ignored
-
The valve was not designed for the actual service cycle
Experienced engineers rely on a combination of:
-
Design codes
-
Manufacturer data
-
Project experience
-
Feedback from operation and maintenance teams
This practical mindset is what ultimately ensures pipeline safety and reliability.
Conclusion
Choosing the right valve for a natural gas pipeline is a multidisciplinary engineering decision involving fluid dynamics, materials science, safety standards, and operational experience.
By focusing on real operating conditions, selecting appropriate valve types and materials, ensuring compliance with recognized standards, and considering long-term performance, engineers can significantly reduce risk and improve system reliability.
In natural gas pipelines, a well-chosen valve is not just a component—it is a critical safety barrier.
If you have any technical questions or would like to discuss your specific pipeline conditions, feel free to contact us—we’re always happy to exchange engineering insights.